Last Updated: 4 February 2026
Understanding Poker Ranges: Charts, Types, and Strategy to Dominate Your Opponents
Learn how to use poker ranges to outplay your opponents. Explore range charts, types, and strategies for preflop and postflop success with real game examples.
Guides
Poker hand ranges are one of the most important tools for improving your poker strategy. By understanding ranges, you can predict your opponents’ hands more accurately, allowing you to make better-informed decisions.
For example, Imagine you’re in middle position, holding Ace-Queen suited. You raise, and the player in the big blind calls. Based on their call, you can narrow down their hand range. They likely have hands like middle pocket pairs (6s-9s), suited connectors, or weaker broadway cards (KJ, QJ). Understanding this range allows you to play more strategically on the flop, turn, and river, adjusting your bets or bluffs accordingly, rather than guessing their exact hand.
This guide will walk you through poker ranges, including charts, types, and real-game strategies, helping you to dominate your opponents.
What is Poker Range?
A poker range refers to the spectrum of possible hands a player might have in any given situation. Instead of guessing a single hand, advanced players of both real life and online poker assess a range of potential hands their opponent could hold. This allows for more accurate decision-making, as poker is a game of probabilities rather than certainties.

Let’s say you’re on the button, and a player in early position raises preflop. Based on their early position, you can assume they have a tighter range, likely strong hands such as high pocket pairs (like QQ, KK, or AA) or big suited connectors (like AK, AQ). Now, if you hold something like pocket 9s or AQ suited, you need to consider whether these hands perform well against that tighter range.
Understanding how these combinations are distributed between suited and offsuit hands is key to reading your opponent’s range. For instance, if an opponent raises preflop from an early position, you can reasonably assume they have a tighter range. This knowledge allows you to make better decisions about your own hand.
Poker Range Charts
Players often use visual tools that help assess the likelihood of certain hands within an opponent’s range. These poker range charts break down all possible starting hands into a matrix, allowing you to see how different combinations (like pairs, suited, and offsuit hands) fit within a given range. By using these charts, players can more accurately estimate an opponent’s hand strength based on their position and actions during the game.
The charts are typically read in four ways: by the hand’s suitedness, pairing, percentage, and combos. Each method provides unique insights into how to evaluate hands in different scenarios. These charts help players make better decisions during key moments in a poker game, like deciding when to bet, raise, or fold.
Poker Hand Range in Matrix
Ranges are often visualized through a matrix or grid, which maps out 169 potential starting hands (13 x 13 combinations). These hands consist of pairs (e.g., AA, KK), suited hands (e.g., Ace-King suited or AKs), and offsuit hands (e.g., Ace-King offsuit or AKo). While the grid only displays 169 combinations, when considering all four card suits, there are actually 1,326 unique hand combinations.
For example:
- Ace-King suited (AKs) has four possible combinations, one for each suit pairing (hearts, spades, clubs, diamonds).
- Ace-King offsuit (AKo) has 12 combinations.
- The cell where the row for Ace and column for King meet would represent Ace-King suited (AKs) or offsuit (AKo) based on its position in the grid.
The matrix is divided into categories like suited hands, offsuit hands, and pairs. Each hand type offers different strategic advantages. Suited hands have higher flush potential, while pocket pairs increase your odds of hitting trips or full houses. This clear visualization allows players to quickly gauge their own or their opponent’s hand strength.

In a real game, you can use the matrix to estimate the range of hands your opponent is likely playing based on their position and actions. For instance, if a player raises from an early position, they’re more likely holding strong hands like pocket pairs or suited connectors. In contrast, a late-position player might have a wider range, including weaker hands like suited connectors (e.g., 76s) or lower pairs. Using the matrix helps you assess ranges effectively, guiding you on better decisions.
Poker Range Range in Percentage
A poker range in percentage refers to the portion of all possible starting hands that a player might play in a given situation. This is typically expressed as a percentage of the 1,326 possible hand combinations.
For instance, a “10% range” means the player is only playing the top 10% of hands, which includes premium hands like AA, KK, AKs, and AQo. The percentage tells you how wide or narrow the range is, with lower percentages indicating a tighter, more conservative range and higher percentages representing a looser, more aggressive range.

Using percentage ranges allows you to quickly assess the strength of an opponent’s potential hands based on their position or betting action. For example:
- A player in early position might only play a tight 10-15% of hands, focusing on strong pairs or premium suited hands.
- Players in mid-position might widen their range to 15-30% of hands, allowing them to play a greater number of holdings.
- A player on the button or in late position may expand their range to 30-40%, including weaker hands like suited connectors and lower pairs.
Knowing the percentage range helps you adjust your strategy. If you know an opponent plays a 20% range from late position, you can estimate the types of hands they might hold and counter their moves. For instance, if they bet aggressively, you can decide whether to continue in the hand based on the likelihood that their hand falls within that range. This strategy improves your ability to make informed decisions, from bluffing to calling down bets.
Poker Range Combos
The specific number of possible card combinations for each starting hand in a player’s range are known as range combos. Each hand in the deck can form multiple combinations depending on whether it’s suited or offsuit. For example, there are:
- 16 possible combinations of unpaired hands like Ace-King (AK).
- 12 being offsuit (AKo).
- 4 being suited (AKs).
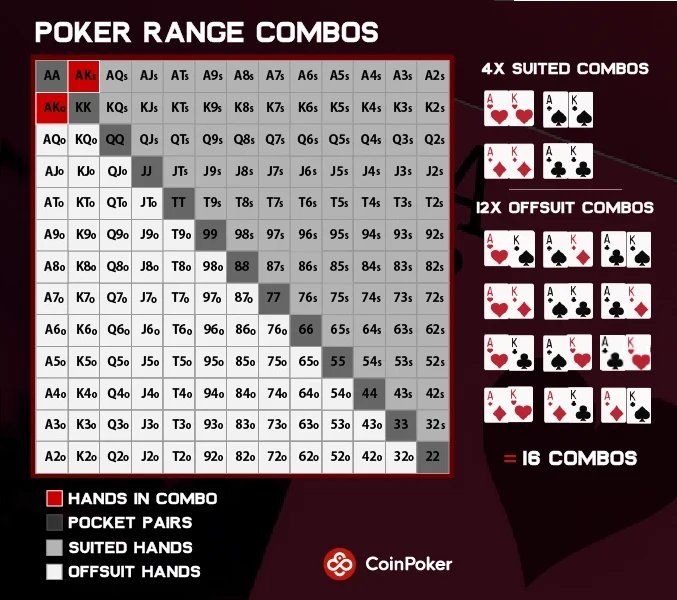
The concept of combos allows you to estimate how often certain hands appear in a given range. Paired hands such as pocket aces (AA), have 6 possible combinations, while suited hands like AKs have only 4 combinations. This breakdown informs you of the likelihood of facing a specific hand. Knowing how many combos an opponent can have of a particular hand allows you to make better predictions about their range.
Counting combos helps you assess how strong your hand is relative to an opponent’s potential holdings. For instance, if an opponent’s range includes many suited connectors or low pairs, you can determine how often they might hold flush or straight draws. If you’re facing a large bet, you can estimate how many combinations of strong hands they could have versus bluff hands. This gives you a better sense of whether to call, raise, or fold in crucial moments.
Poker Range Strands
Specific groupings of hands that fall within a player’s potential range are referred to as range strands. These groupings are often expressed using shorthand notations like 22+ or JT+, which help players quickly visualize hand ranges. For example:
- 22+ means any pocket pair from twos (22) and higher.
- JT+ includes suited and offsuit combinations of jack-ten and stronger hands like QJ, KQ, and AK.

Strands provide a simple way to represent a group of hands that players might use based on their position and game strategy.
The benefit of using poker range strands is that it allows players to break down large sets of hands into manageable groups. By understanding the shorthand, you can more easily assess what your opponent might hold. For instance, 22+ indicates a range of pocket pairs that may be played more conservatively, while JT+ typically represents connected hands that can form straights and high pairs. This makes it easier to categorize an opponent’s potential holdings and predict their moves.
In real games, poker range strands help you make faster decisions by narrowing down your opponent’s likely hands. For instance, if someone raises preflop from an early position, you might assign them a range like 22+ and AK+, assuming they are playing strong pocket pairs and premium hands. A late-position player might be playing a wider range like JT+, representing hands that are more speculative but still have drawing potential.
How to Calculate Poker Hand Range
In poker, players do not know their opponents’ hands, but by analyzing betting patterns and positions, they can assign an estimated range of hands. For example, if an opponent raises from an early position, their range is likely tight and strong, while a late-position raise might indicate a broader, more speculative range. Calculating a hand range is a dynamic process that evolves as the game progresses, influenced by both preflop and postflop actions.
Position is Power
Position in poker is a vital factor in calculating a hand range. Players in early positions like Under The Gun (UTG) are expected to play tighter ranges, as they must act before others. In contrast, players in late positions like the button (BTN) or cutoff (CO) can afford to play wider ranges since they have more information about their opponents.
For example, an early position player might play a range of 10-15% of the strongest hands (like pocket pairs 88+, AK, AQ), while a late-position player could expand their range to 30-40% of hands (including hands like JTs, suited connectors, and lower pairs). Understanding positional dynamics helps calculate the likelihood of what hands an opponent could hold based on when and how they enter the pot.
Example of Hand Ranges Based on Position:
| Position | Example Hand Range |
| Early (UTG) | 10-15% (88+, AK, AQ) |
| Middle (MP) | 15-20% (77+, AJs, KQs) |
| Late (CO, BTN) | 30-40% (22+, JTs, QTs) |
| Blinds | Varies (Steals, Traps) |



Bet Sizing and Aggression
Betting behavior is another key factor in calculating hand ranges. Larger bets or aggressive moves often indicate stronger hands, while smaller bets or checks might suggest a wider, weaker range. For instance, if an opponent makes a large preflop raise, you can assume they are likely holding premium hands like AA, KK, or AK. On the other hand, a small bet might indicate a speculative hand like suited connectors (e.g., 67s) or a mid-range hand like KJ.
Observing how often a player bets or raises, along with the size of their bets, gives you clues about the strength of their range. By consistently analyzing bet sizing, you can refine your understanding of their possible hand combinations.
Example of Betting Behavior and Hand Strength:
| Betting Action | Likely Hand Range |
| Small Bet or Check | Weak or speculative hands (e.g., 67s, 22-66) |
| Moderate Bet | Mid-range hands (e.g., KJ, QJs) |
| Large Bet or Raise | Premium hands (e.g., AA, AK, KK) |
| All-in or 3-bet | Strong hands or bluffs |
Opponent Tendencies and Play Style
Understanding your opponent’s tendencies is crucial in calculating hand ranges. Some players are naturally more aggressive, consistently raising with a wide range of hands, while others are tighter and only raise with premium hands. By paying attention to how an opponent plays over time, you can better gauge the range of hands they might be willing to play.
For example, a loose-aggressive (LAG) player is more likely to have a wide, unpredictable range that could include bluffs, while a tight-aggressive (TAG) player is more likely to be playing a narrower, stronger range. This understanding helps in narrowing down the range of possible hands an opponent may hold based on their actions.
Board Texture
The community cards significantly affect how you calculate a hand range. Certain board textures will interact more with certain ranges. For example, a flop of low, connected cards (e.g., 6-7-8) may favor hands like suited connectors or small pairs. A high-card flop (e.g., K-Q-2) would more likely connect with a tighter range consisting of broadway cards like AK or AQ.
Evaluating how the board changes an opponent’s range throughout the hand allows you to adjust your calculations and respond accordingly. If the board is highly coordinated, an opponent’s betting or checking may signal that their hand connects well with the texture or that they are cautious of potential draws.
Calculating Preflop Hand Range in Poker
The preflop hand range is the selection of hands a player is willing to play before the community cards are dealt. This range varies based on position and playing style. Players in earlier positions, like Under the Gun (UTG), adopt a tighter range, while late-position players can afford to play a wider range. For example:
- UTG typically plays 10-15% of hands, focusing on premium hands like high pairs and strong suited hands.
- Middle position (MP) players expand to 15-30%, including hands like 77+, AJs, KQs, and KTs.
- Late position (CO, BTN) players can play 30-40%, including speculative hands like suited connectors and small pairs.
Preflop ranges are important for building a solid poker strategy. Recognizing when to adjust your range based on position and your opponent’s preflop tendencies allows you to make informed decisions.
Calculating Postflop Hand Range in Poker
Postflop hand ranges refer to the possible hands a player might hold after the community cards are dealt. Unlike preflop, postflop ranges become more refined as player actions and community cards provide more information.
After the flop, the preflop hand range narrows based on betting patterns and the flop’s texture. For example:
- A player raising from Under the Gun and continuing to bet postflop likely holds overpairs (AA, KK) or strong top pairs (AK, AQ).
- Continuation bets from late position players can represent a broader range, including suited connectors, middle pairs, or bluffs.
As more community cards are revealed, the likelihood of specific hands becomes clearer. For example:
- A wide preflop range like T9s or 22 may connect with the flop, hitting a straight draw or set.
- On an Ace-high flop, weaker hands are often eliminated from cautious players’ ranges, leading them to fold.
How to Use Poker Range to Improve Your Game?
Using poker ranges effectively can dramatically improve your game by helping you make more informed decisions. By calculating your equity against different ranges, you can decide when to execute value betting if you believe your hand is ahead of your opponent’s range. That extracts the most chips when you’re favored to win.
Outplaying Opponents with Ranges
One of the most powerful ways to outplay opponents is by correctly estimating their hand ranges. By understanding the range of hands your opponent is likely to hold, you can tailor your strategy accordingly.
For example, if a tight player raises from an early position, they likely have a strong hand range, including high pairs or premium hands like AK or AQ. Knowing this can help you fold weaker hands. Alternatively, if a loose player in a late position opens with a wider range, you can take more risks, knowing that they could be holding weaker hands.
Balancing Your Own Range
Balancing your own hand range is another essential aspect of poker strategy. This means mixing up your play to prevent becoming too predictable. If your opponents can always guess that you’re only raising with strong hands they’ll adjust by folding their weaker hands. Instead, balance your range by occasionally including semi-bluffs with hands like suited connectors (9-8 suited) or small pocket pairs. This keeps your opponents guessing, as they’ll have a harder time reading whether you’re holding a premium hand or something more speculative.
Adapting to Game Flow
Ranges are not static; they shift based on your position, the actions of your opponents, and the community cards. As the game progresses, refine your understanding of what hands your opponents might have based on how they’ve played their preflop and postflop ranges. By staying flexible and adjusting your strategy as ranges evolve, you gain a significant advantage.
Bringing poker ranges into your game lifts your understanding of poker from individual hand strength to a more sophisticated, strategic approach. By mastering ranges, you’ll play more effectively, maximizing wins while minimizing losses.
Real Game Examples of Using Poker Range
In real poker games, using ranges effectively helps you predict opponents’ hands and adjust your play accordingly. Below are two examples that demonstrate how understanding poker ranges allows you to make informed decisions on the turn and river, using range shifts to your advantage.
Game 1
You’re in the big blind, and the button raises preflop. Knowing that players often raise with a wide range from the button, you estimate their hand range to include broadway cards (K-Q, Q-J), suited connectors, and possibly mid-pairs like 7-7. You call with 10-9 suited.
The flop comes 8-6-2 rainbow. While you miss the flop, this board likely hasn’t hit the button’s wide range. Given the button’s continuation bet, you know they could be holding two overcards like A-Q or K-J. You decide to check-raise, representing a set or strong draw. The button folds, showing that your read on their range was correct (they were likely bluffing with overcards).
Game 2
You’re on the button holding A-Q offsuit, and an early-position player raises. Knowing their range from this position is tight (typically including strong hands like A-K, Q-Q, and K-K) you decide to call and see the flop.
The flop comes A-10-3, giving you the top pair. The early-position player makes a strong continuation bet, which narrows their range further to include hands like A-A, A-K, A-Q, or A-J. With the top pair and Q kicker, you call.
The turn brings a 5, and again you call their bet.
On the river, an irrelevant 2 falls, and they check. This shift in their betting pattern now indicates a possible missed draw or weaker ace, allowing you to confidently value bet. Your opponent calls and reveals A-J. You win with a slightly better kicker.
In both examples, understanding ranges helped guide your decisions at critical moments, allowing you to turn the situation in your favor.
Tips to Consider when Using Poker Hand Ranges
When using poker hand ranges effectively, it’s crucial to develop a strategic approach that can adapt to different game situations. By understanding how to manipulate your range based on factors like position, opponent behavior, and board texture, you can significantly improve your decision-making and outplay your opponents. Here are seven practical tips to help you make the most of poker hand ranges in real games:
- Adjust your range based on position
In earlier positions, play a tighter range, as you’re acting first. In later positions like the button, you can widen your range because you have more information on how opponents are playing. - Pay attention to opponents’ tendencies
Study your opponents’ betting patterns. If they often raise preflop with a wide range, you can counter by playing tighter or exploiting them with strategic bluffs on later streets. - Balance your range to avoid predictability
Don’t always play the same hands in similar situations. Mix in some strong hands with bluffs to keep your opponents guessing about your true range and avoid being easily read. - Narrow ranges based on postflop action
Use your opponent’s betting behavior postflop to further narrow their hand range. A strong continuation bet can indicate a premium hand, while a check or small bet might suggest weakness. - Understand board texture and range interaction
Some flops favor wide ranges, while others are more beneficial for tight ones. For example, low connected boards often hit tighter ranges, while high cards are more favorable to wide ranges. - Use a poker range calculator for precision
For online games, leverage poker range calculators to quickly assess which hands are likely in your opponent’s range, allowing you to make more informed decisions. - Don’t overestimate your range
Just because you have a wide or strong hand range doesn’t mean you’re invincible. Always be mindful of how the board develops and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Conclusion
Mastering poker hand ranges is essential for improving your game and making better decisions. By understanding how to read ranges, you can outplay your opponents. Whether it’s calculating preflop ranges, adjusting based on position, or reading your opponent’s hand, mastering these skills will give you a significant edge.
Ready to take your game to the next level? Join CoinPoker today to test your skills, compete in exciting games, and put your newfound poker range knowledge to the test.
FAQs
A poker hand range is the spectrum of possible hands a player could have based on their actions. It helps players assess their opponents’ hands and make informed decisions in different situations.
Poker ranges help players better predict their opponents’ moves, allowing for more strategic play. By understanding ranges, you can make better calls, bluffs, and raises.
Calculating a poker range involves considering position, betting patterns, and previous actions. Tools like range charts and poker calculators simplify this process.
Yes, poker ranges evolve from preflop to postflop based on the community cards and opponents’ actions. Adjusting your range accordingly is crucial for optimal play.
Explore More
Announcements
Read recent announcements from CoinPoker about new games, ambassadors, and changes to our platform.
1 PostGuides
The go-to resource for mastering poker with expert tips and strategies. Our guides will elevate your poker skill level.
60 PostsNews
Find the latest poker news and latest CoinPoker Newsletters. Get updates about games, promotions, and crypto news.
96 PostsPromotions
Find the latest coinpoker promotions here. Explore the crypto poker world with the best poker promotions available.
1 Post
















