Smart Contracts and Gas: How CHP Withdrawals and Deposits Work
For those of you who are new to cryptocurrency transfers, terms like gas, Gwei, and network congestion can be confusing. In light of recent events on the ETH blockchain that resulted in withdrawal delays, we want to make sure our players understand how the system CHP tokens operate on works.
As far as money is concerned, transparency is the best policy. That is why we recommend reading the following guide, which will help you understand the protocols and factors involved in speeding up, or slowing down, your payments.
How Your CoinPoker Deposits and Withdrawals Work
Before we dive into the general stuff, we want to clarify a few things about how payment processing works at CoinPoker:
- All CoinPoker payments (mainly withdrawals) are sent to the ETH network immediately; we do not have any blocks or extra protocols in place to slow this down.
- The amount of time it takes to process is determined by the speed of the ETH network, which we will get into next.
With the exception of cases where security breaches are reported, we do not hold up your deposits or withdrawals with extra screening. Once a withdrawal is requested, it is out of our hands, and into an immense environment comprised on ETH Smart Contracts.
Transactions on the ETH Network Explained
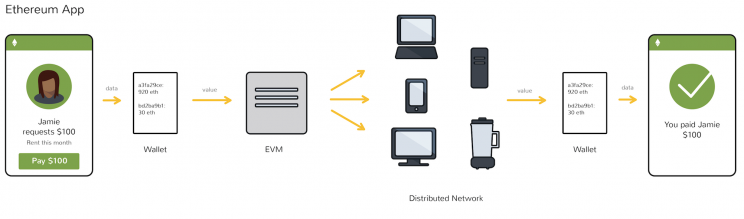
In order to understand how your CHP moves from an exchange to your wallet to CoinPoker, you need understand a few key concepts:
- Smart Contracts
- Gwei (or Gas) Price
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
If you’ve read our “What is CHP” guide, you already know that the tokens used on CoinPoker are classified as ERC-20 tokens. All this means is that they have been built on the Ethereum network and is transferred between accounts using smart contracts.
What Are Ethereum Smart Contracts?
Many people are confused by the term “smart contracts”, and CoinDesk’s handy information section explains the reasons for this confusion quite well:
While a standard contract outlines the terms of a relationship (usually one enforceable by law), a smart contract enforces a relationship with cryptographic code. Put differently, smart contracts are programs that execute exactly as they are set up to by their creators.”
Smart contracts are what makes the ETH network tick, and in the case of CHP, they are used to transfer funds from one user to another (usually our platform and yourself). But the use of Smart Contracts is not limited to currency transfers, and depending on the token they can also be used to store information, handling insurance policies, loans and more
In the case of CHP tokens, they are used to power deposits and withdrawals to and from CoinPoker.
What is Gwei and Why Do I Need It to Transfer CHP?
Gwei is required when any smart contract is created on the ETH Network. It is best explained as a transaction or processing fee for validating the smart contract. This gas price does fluctuate on a daily (and even hourly) basis depending on how busy the Ethereum network is.
Considering the amount of ERC-20 tokens out there, there’s a lot of traffic in terms of Smart Contracts being sent out and validated by the network. More congestion means more processing for the ETH network, hence the increase in transaction fees (a.k.a. Gas and Gwei).
Is there a difference between gas and Gwei?
When you hear the term gas, is usually refers to the gas limit, while Gwei refers to the gas price in a unique unit of measurement (1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH). Together, these two values help you determine the cost of transaction, which is referred to as Tx.

The gas limit is the volume of gas required, while Gwei is the price for each unit. Depending on the token and network activity, the amount of each required may vary. MyEtherWallet has a great analogy on their helpful guide explaining how gas works:
You can think of the gas limit like the amount of liters/gallons/units of gas for a car. You can think of the gas price as the cost of that liter/gallon/unit of gas.”
In the case of CHP, 60,000 Gas and is enough for depositing, for Gwei always check ETH Gas Station for the most up to date price. You can also adjust the Tx you pay to have your transactions processed faster or slower using various tools on ETH Gas Station.
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine?
Simply put (perhaps too simply), the Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM is the part of the Ethereum blockchain that processes and executes smart contracts. If you do not pay a high enough Tx, the EVM will not execute the transaction and it will fail.
Because gas price (and therefore Tx) can fluctuate so much based a wide range of factors, it can be tricky during extreme situations.
For example:
CoinPoker automatically calculates the gas price with a formula that takes the median value based on the last thousand transactions. This amount is then applied to the withdrawal, which has proven to be effective and accurate in the past. That is, when network fluctuations are within the expected range.
Recent CoinPoker Withdrawal Delays Explained
During the past week, gas prices were inflated drastically by a clog in the network. So much so that the value exceeded the estimation made by the formula. This resulted CoinPoker withdrawals being sent to the EVM with a Tx that was too low, leaving them “Pending” and unalterable until the network gets around to dealing with them.
Not only does this leave a few unlucky players waiting, but these transactions block the queue of all subsequent withdrawals. As blockchain networks and crypto services like CoinPoker become more popular, incidents like this will be easier to anticipate.
With new comes new challenges, and if you have any questions about CoinPoker, CHP, or general crypto topics join our community on Telegram, or send an email to [email protected]/fr.
Cet article vous a été utile ?
Vous ne trouvez pas ce que vous cherchez ?
Contactez-nous et dites-nous comment nous pouvons vous aider.
Nous contacter